When working on a machine learning project, choosing the right error metric or evaluation metric is critical. This is a measure of how well your model performs at the task you built it for, and choosing the correct metric for the model is a critical task for any machine learning engineer or data scientist. IoU is mainly used to evaluate object detection models.
How to use evaluation metrics
For Zindi competitions, we choose the evaluation metric for each competition based on what we want the model to achieve. Understanding each metric and the type of model you use each for is one of the first steps towards mastery of machine learning techniques.
Intersection Over Union(IoU) as an evaluation metric
Intersection over Union is the measure of overlap between two bounding boxes; it calculates the overlap between two objects, divided by the total area of the two objects combined.
To apply IoU to object detection algorithm, we need:
1. The ground-truth bounding boxes (the true values specify where the object is in our image).
2. The predicted bounding boxes from our model.
Intersection Over Union(IOU) between 2 bounding boxes:
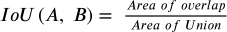

Let’s look at each box representation, i.e (left, top) and (right, bottom). For box 1 the representation is [ (x1, y1), (x2, y2) ] while Box 2 is [ (x3, y3), (x4, y4) ]
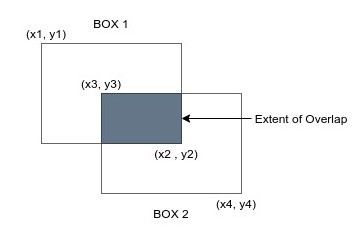
Step 1: Calculate the Area of Overlap
Let’s look at the representation below of the intersection between the two boxes. How do we calculate the coordinates (x, y) for the overlap area? How do we get [ left(x), top(y), right(x), bottom(y) ].
The coordinates for box 1 are represented by [ (x1, y1), (x2, y2) ] while those of Box 2 are[ (x3, y3), (x4, y4) ]
The [ left(x), top(y), right(x), bottom(y) ] of the overlap is calculated by:
x_left = max(x1, x3)
y_top = max(y1, y3)
x_right = min(x2, x4)
y_bottom = min(y2, y4)
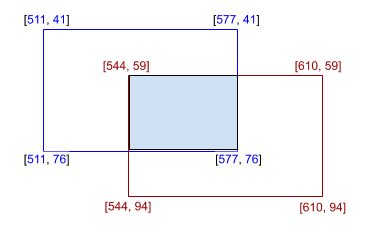
Using the examples above where box 1 coordinates are (511, 41, 577, 76) and box 2 coordinates are (544, 59, 610, 94). The coordinates of the overlap box will be:
x_left = max(x1, x3)
= max(511, 544)
= 544
y_top = max(y1, y3)
= max(41, 59)
= 59
x_right = min(x2, x4)
= min(577, 610)
= 577
y_bottom = min(y2, y4)
= min(76, 94)
= 76
The coordinates of the overlap are: (544, 59, 577, 76)
Now that we have the coordinates, the area of overlap is the area of the rectangle formed:
Width = x_right - x_eft
Height = y_bottom - y_top
Area of overlap = width * height
Step 2: Calculate the Area of the Union
As seen earlier, the union area is the total area covered by the boxes.
box 1 area = width * height
box 2 area = width * height
Area of Union = box 1 area + box 2 area - area of overlap
Step 3: Calculate the Intersection Over Union(IOU)
Intersection Over Union = Area of Overlap
__________________
Area of Union
For object detection models you want to maximise your IoU score as you want your Area of Overlap to equal your Area of Union.
With this knowledge, you should be equipped to use IoU for your next machine learning project.
Why don’t you test out your new knowledge on one of our knowledge competitions that use IoU as its evaluation metric? We suggest the Local Ocean Conservation - Sea Turtle Face Detection